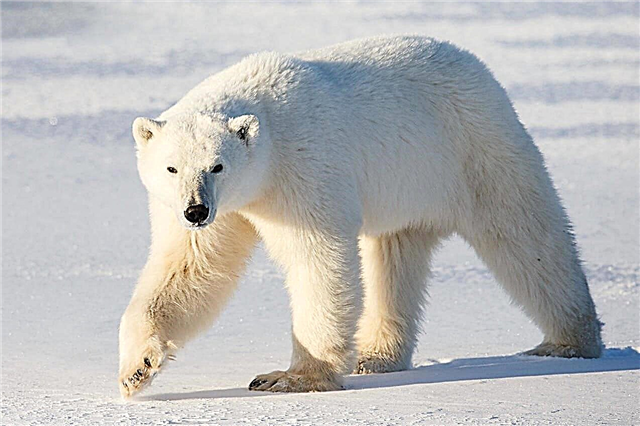
The polar bear is the world's largest terrestrial carnivore living in the Arctic: in the remote northern regions of Greenland, Norway, Canada, Russia.
And while northern bears traditionally look white, it is amazing, but their coat is devoid of white pigment, in fact it is translucent, and its skin is black. So why is a polar bear a white? The answer to this question is given by the research of scientists about what the polar bear's wool consists of, as well as the study of optical phenomena that affect the color of the fur of this animal.
Interesting fact: The polar bear is the largest land predator on Earth. The length of the animal is about 3 meters, weight - up to 1 ton.
What does polar bear hair consist of?
The polar bear's hair contains two layers of hairs: the outer protective layer, consisting of long (5-15 cm) outer hairs; and a dense insulating undercoat, the hairs of which are shorter and thinner than in the protective layer.

Properties of protective wool:
- translucent;
- hollow, i.e. empty inside;
- coarse, narrowed (gradually reaching the base);
- contain particles that scatter light;
- contain salt particles;
- consist of keratin protein.
The translucent fur of the bear’s fur appears white also due to the thickness of the animal’s hair.
The influence of optical phenomena
The polar bear's coat is translucent, but due to the properties of the protective hairs that are involved in creating the optical effect, these animal fur seems white.From the point of view of optics, the reason why the polar bear appears white is due to the effect of light on the animal's hairline.
Luminescence

When the sun's rays fall on the hair of a polar bear, part of this light falls into a kind of trap in the hairs. This light energy is beaten off inside the hollow part of the hairs, causing a reaction that is the emission of light - luminescence. This happens every time a ray of light contacts the animal’s hair.
Luminescence is accelerated by light scattering particles in the hairs, which destroy the beam of light. When light enters a light-scattering particle, it breaks up into a larger number of rays that move in different directions. Particles of light scattering are found both on the inner surface of the hairs and on the outer. The scattering of light leads to the appearance of a larger amount of white color and its further emission by the hairline of the animal. Thus, the translucent bear’s fur reflects sunlight. This is the reason polar bears are especially bright in direct sunlight. The brighter the lighting, the more light is reflected by the translucent hair of the polar bear.
Salt particles

Polar bears spend a lot of time in water, which is the reason for the Latin name of these representatives of the bear family ursus maritimus, which means “sea bear”. Polar bears collect salt particles while swimming or staying near saltwater.Salt particles along the rough surface of the wool also act as light scattering particles, which increase the amount of light rays and enhance luminescence.
Ultraviolet light

When the sun shines on a polar bear, ultraviolet light along the protective hairs descends to their base and penetrates the dark skin of the animal. When ultraviolet light enters the skin, it causes a whitish color due to fluorescence (the ability to give off absorbed energy in the form of cold light radiation). Fluorescence is a type of luminescence. Thus, ultraviolet radiation also causes the white color of the bear’s coat.
Interesting fact:Ultraviolet rays, which are transmitted through translucent hairs, give the polar bear's wool thermal insulation properties.
Keratin
Keratin is a common natural protein found in the skin, nails and hair. Like humans, bear hair contains keratin. The protein molecules of keratin emit a whitish color, which further contributes to the appearance of a white coat in a bear.
Why does a polar bear change color?
Now that it’s known why polar bears are white, it’s interesting to know why some of them get a yellow, brownish or even green hue.

With changes in the season, habitat, and wool that grows throughout the year, slight differences in the color of the polar bear's fur are noticeable, which helps him adapt to the environment.At the end of autumn and winter, when polar bears change their fur and new hair grows, they look whiter than in summer, when the fur becomes yellowish due to wear and constant exposure to the sun. Bears that live on ice far from the water appear whiter than bears that swim a lot. Polar bears on land with little or no snow wear light brown fur.
The coat of polar bears that live in warm conditions (for example, in zoos) sometimes takes on a green tint. This is because algae growing in water bodies colonize the internal environment of bear’s hollow hairs and reflect the green color. Algae do not grow in the cold Arctic north, so the polar bears that live in the Arctic remain white. This helps them disguise themselves when hunting, merging with the snow-white Arctic atmosphere.

Polar bears are amazing animals that are even adapted in color to their arctic home.
Having black skin and translucent hair, the polar bear looks white due to the structure and properties of the hairs, which have free space inside, and the light that penetrates them and creates luminescence. The white color of the translucent bear’s fur is also imparted by ultraviolet light, causing fluorescence, and keratin, whose molecules emit a whitish color.
Each of these elements supports the white color of the hair of a polar bear. Thus, the polar bear’s fur reflects a lot of light, therefore it is white.