It is known that all substances are composed of molecules. But what are the molecules themselves made of? Let's look at this issue in more detail.
What is a molecule?
The name "molecule" comes from the Latin molecula - it is a diminutive of the word moles (mass translated). Their existence was first proven in an experiment in 1906 by J. Perrin, a French physicist, when he studied Brownian motion.

In chemistry, this is the name of a separate particle of matter, which consists of 2 or more atoms linked together by covalent bonds. Quantum mechanics defines it as a system consisting not of atoms, but of their nuclei and electrons interacting with them.
Interesting fact: Physics calls molecules not only polyatomic particles, but also monatomic ones, consisting of atoms not connected by chemical bonds (pure mercury or inert gases). In this case, the concepts of “molecule” and “atom” are combined.
Usually the molecules are electrically neutral, since the number of protons and electrons in them is the same, but there are molecules that have an electric charge (they are called ions).
Particles of a substance with a high molecular weight are called macromolecules. They consist of proteins, nucleic acids, enzymes, polysaccharides, amino acids, complex lipids and individual artificially created compounds, for example polymers. They include hundreds and thousands of atoms. Derivatives of hydrocarbons - organic substances and biopolymers, as a rule, not only have a large mass, but are also more complex than inorganic compounds.
Molecular structure
The molecule of any compound has the same composition, it always has the same number of atoms, chemical properties depend on the valence bonds that hold them together. The classical theory considers the molecule as a dynamic structure consisting of atomic nuclei and their groups and a certain number of electrons located on internal and external levels.
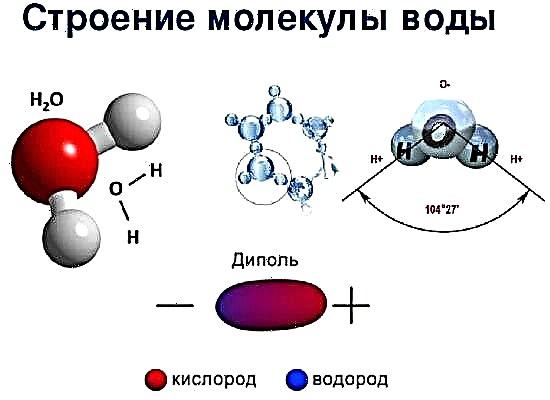
Chemical bonds usually form only external electrons. A bond is created by 1,2 or 3 pairs of electrons of 2 neighboring atoms (as a result of which an electron cloud appears). The interaction energy of atoms depends on the distance at which they are located, and contributes to the stability of the molecule under ordinary conditions: it does not allow atoms to get too close together.
Atoms can be charged positively and negatively; their number is always constant. The structure and composition of the molecules of a certain substance is not affected by the way it was obtained, that is, an artificially produced substance will be exactly the same as natural.
The molecular composition is written using chemical formulas. The structure determines what physical properties a substance will possess.
Interesting fact: organic matter, water, carbon dioxide melt and boil at relatively low temperatures, and retain their structure in the solid state. Many inorganic substances do not consist of molecules, but of atoms (crystals, pure metals, etc.).
Molecules in science
In chemistry this is the basic concept, the molecular structure is determined on the basis of chemical reactions with a substance.It is also possible, knowing the structure, to establish what the reactions will be. As a result of chemical studies, the bulk of knowledge about molecular functionality and structure was obtained.
The structure in physics explains the physical properties of liquids, gases, and solids. The mobility of the molecules determines how quickly a substance is able to penetrate into another upon contact, the level of viscosity and the thermal conductivity.
In biology, molecular properties and spatial structure are of paramount importance, since all living things function due to the delicate balance of the interaction between molecules (chemical and non-chemical).
The question of what molecules consist of can be answered this way - from a certain number of atoms joined together by chemical bonds. All substances on the planet are made up of molecules.whose physical and chemical properties are determined by the structure and composition of the molecules.