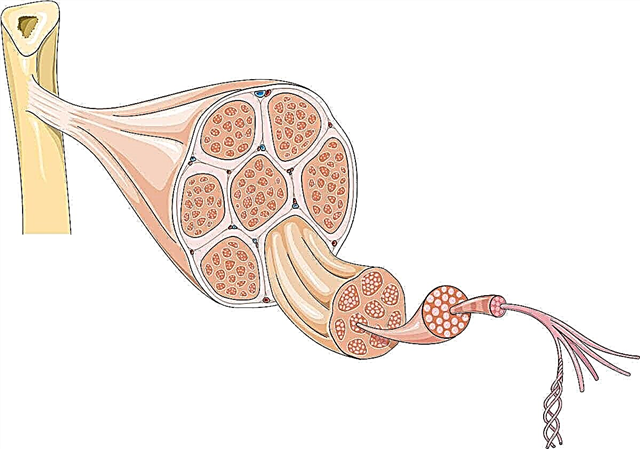
In the event of a hypotonic crisis of the sites of ribosomal genes, non-standard abnormal structures are formed.
Russian scientists conducted studies, as a result of which they were able to establish the effect of hypotonic stress on the features of the process of provoking gene formation in ribosomes. Thanks to this, they established how the formation of anomalies and the possibility of preventing them occur. Research data was provided in the scientific publication Nucleic Acids Research.
Ribosomal inclusions are organelles that are of great importance for the functioning of living cells, namely in the course of processes such as the biosynthesis of protein compounds and aminocarboxylic acids, known as translation. They proceed with the obligatory participation of the ribonucleic acid matrix, in which the gene structures are located, transport ribonucleic acid, which transfers the amino acid to the ribosomes. Ribosomes include RNA and protein (1: 1).
For research, scientists used cancer cells and cells of a healthy person. When water enters the cells, their volume increases. In this case, the formation of the R-loop is in the regions of the ribosome genes.
Non-derivative structures have the form of hybrids from ribo- and deoxyribonucleic acids. These hybrids are extremely dangerous for the body, leading to the breaking of the DNA chain and the formation of an unstable state of the genome.
If the human body is under stress, the likelihood of stress increases several times, leading to the appearance of various ailments.
These studies will help to further determine the nature of the occurrence of cancer, as well as such a dangerous disease as Tricher Collins syndrome (deformation of the craniofacial part of the skull).